Crafting the Offer: Products
Customer Experience Management
Customer experience management (CEM)[1] refers to the strategies and practices that a company employs to design and deliver positive interactions with its customers across all touchpoints throughout the customer journey[2]. It involves understanding customer needs, preferences, and behaviours, and using those insights to create personalized, seamless experiences that meet or exceed customer expectations. The goal of CEM is to foster customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy by ensuring every interaction with the brand — whether through the website, social media, customer service, or in-person — is consistently positive and aligned with the company’s brand values and customer-centric approach.

Services marketing heavily relies on creating memorable customer experiences and building long-term relationships with customers. This chapter includes sections on customer journey mapping, experience design, and relationship marketing tactics tailored to the tourism and hospitality contexts.
Service Management Strategies
Managing services effectively requires a strategic approach to ensure differentiation, quality, and customer satisfaction. Below are key strategies used to manage services across various dimensions.
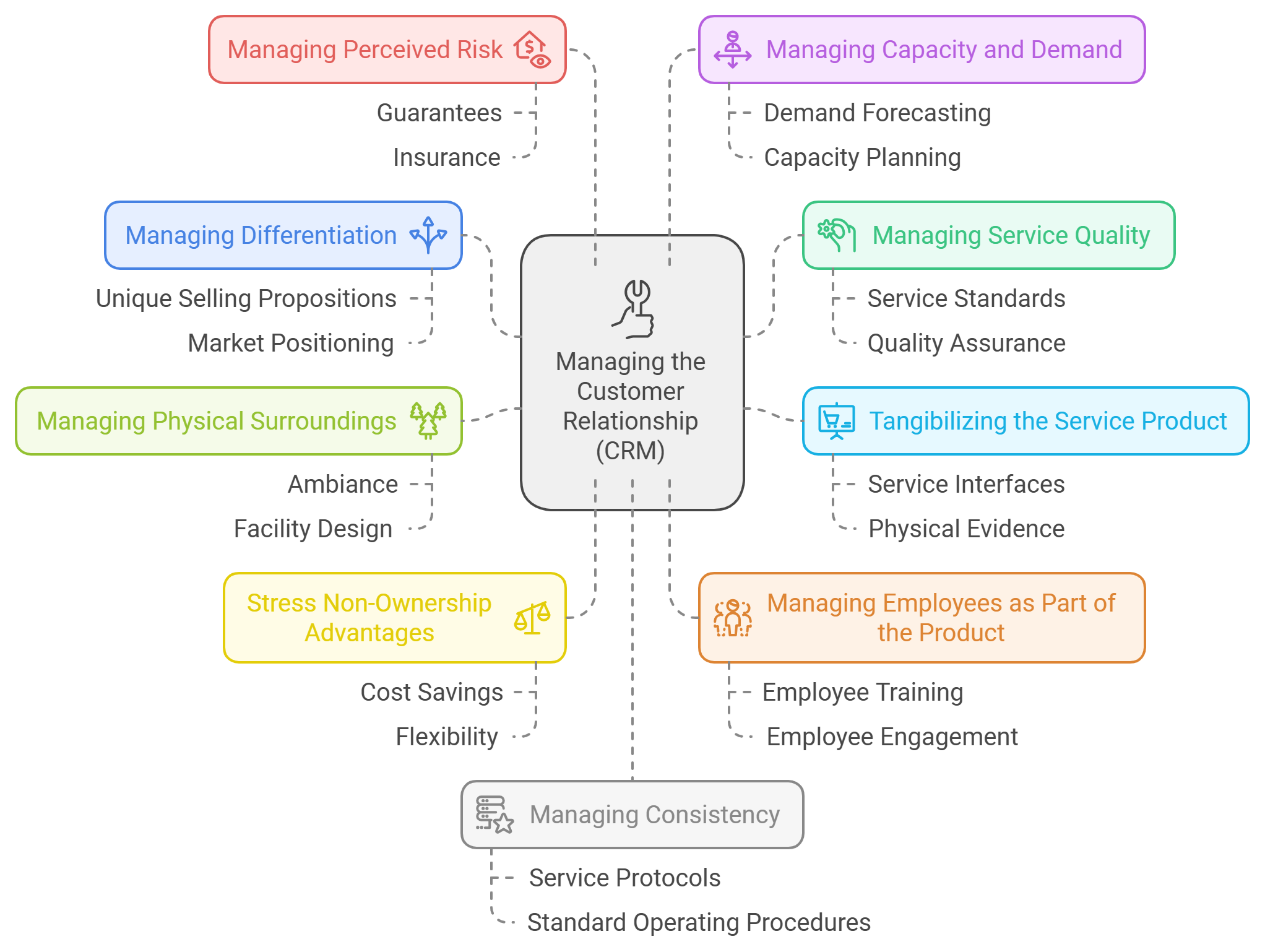
Managing Differentiation:
- Unique Service Features: Differentiate services by offering unique features or benefits that competitors do not provide. This can include personalized customer experiences or exclusive service offerings.
- Branding: Strong branding can help differentiate services in the minds of consumers, making them more recognizable and preferred over competitors.
Managing Service Quality:
- Quality Assurance Programs: Implement robust quality assurance programs to monitor and maintain high service standards. Regular training and feedback loops can help ensure consistent service delivery.
- Customer Feedback: Use customer feedback to continuously improve service quality. This involves gathering insights through surveys, reviews, and direct interactions to identify areas for enhancement.
“Tangibilizing” the Service Product:
- Physical Evidence: Enhance the tangibility of services by focusing on physical evidence such as the appearance of facilities, equipment, and employee presentation. This helps convey quality and builds customer trust.
- Service Environment (Servicescape): Design the physical environment to positively influence customer perceptions and experiences. Elements like layout, decor, and ambient conditions play a crucial role in shaping customer impressions.
Managing the Physical Surroundings:
- Servicescape Management: Strategically manage the physical surroundings where services are delivered to enhance customer experience. This includes optimizing layout, signage, and environmental conditions to facilitate a positive interaction.
Stressing Advantages of Non-Ownership:
- Service Models: Highlight the benefits of non-ownership models such as subscriptions or rentals. Emphasize flexibility, cost savings, and access to the latest offerings without the burden of ownership.
Managing Employees as Part of the Product:
- Employee Training and Empowerment: Equip employees with the skills and authority needed to deliver exceptional service. Empowered employees can enhance customer interactions and contribute significantly to service quality.
- Employee Satisfaction: Foster a positive work environment to boost employee satisfaction, which directly impacts service delivery and customer satisfaction.
Managing Perceived Risk:
- Transparent Communication: Provide clear and accurate information about services to reduce perceived risk among customers. Transparency about service features, costs, and potential outcomes builds trust.
- Guarantees and Warranties: Offer guarantees or warranties to reassure customers about their service choices. This reduces uncertainty and encourages purchase decisions.
Managing Capacity and Demand:
- Dynamic Pricing: Use dynamic pricing strategies to balance demand and capacity effectively. Adjust prices based on demand fluctuations to optimize resource utilization.
- Service Portfolio Management: Regularly assess and adjust the service portfolio to align with market demand and organizational capacity.
Managing Consistency:
- Standardized Procedures: Develop standardized procedures for service delivery to ensure consistency across different locations and touchpoints.
- Quality Control Systems: Implement systems that monitor service delivery processes to maintain consistent quality levels.
Managing Customer Relationship (CRM):
- CRM Systems: Use CRM systems to manage customer interactions effectively. These systems help track customer preferences, history, and feedback, enabling personalized service delivery.
- Omni-channel Integration: Ensure seamless integration across various customer interaction channels (e.g., online, in-store) for a unified experience
Example
The Ritz-Carlton
This luxury hotel chain is renowned for its exceptional customer service and hospitality, which are achieved through several strategic approaches[3][4]:
Managing Differentiation:
Personalized Experiences: The Ritz-Carlton differentiates itself by offering highly personalized guest experiences. They use customer data to anticipate needs and preferences, ensuring each stay feels unique and tailored.
Managing Service Quality:
Empowerment of Employees: Employees at the Ritz-Carlton are empowered to spend up to $2,000 to resolve any guest issue without managerial approval. This empowerment leads to swift problem resolution and exceptional service quality.
“Tangibilizing” the Service Product:
Luxury Amenities and Facilities: The physical environment of the Ritz-Carlton, including its luxurious amenities and elegant decor, helps tangibilize the intangible aspects of hospitality, reinforcing the brand’s premium positioning.
Managing the Physical Surroundings:
Servicescape Design: The hotel’s design and ambiance are meticulously crafted to provide a luxurious and comfortable atmosphere, enhancing the overall guest experience.
Stressing Advantages of Non-Ownership:
Membership Programs: Through exclusive membership programs, guests can enjoy the benefits of luxury hospitality without the commitment of ownership, such as access to exclusive events and experiences.
Managing Employees as Part of the Product:
Comprehensive Training Programs: Employees undergo extensive training to ensure they embody the brand’s values and deliver consistent service excellence. This includes regular workshops and feedback sessions.
Managing Perceived Risk:
Reputation and Guarantees: The strong reputation of the Ritz-Carlton reduces perceived risk for customers. Additionally, their satisfaction guarantees assure guests of a high-quality experience.
Managing Capacity and Demand:
Dynamic Pricing Models: The Ritz-Carlton employs dynamic pricing strategies to manage room availability and maximize revenue during peak demand periods.
Managing Consistency:
Standardized Service Protocols: Consistent service delivery is ensured through standardized protocols across all locations, maintaining the brand’s high standards globally.
Managing Customer Relationship (CRM):
Advanced CRM Systems: The Ritz-Carlton utilizes sophisticated CRM systems to track guest preferences and history, enabling personalized interactions and fostering long-term relationships with customers.
If you are using a printed copy, you can scan the QR code with your digital device to go directly to the video: 15 Things You Didn’t Know About The RITZ CARLTON

Media Attributions
- Figure 1: “Customer experience journey” [created using Canva Magic Studio, with prompt: “Customer experience journey on a winding road”] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Figure 2: “Strategies to manage services” [created using Napkin.ai] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Palmer, A. (2010). Customer experience management: A critical review of an emerging idea. Journal of Services Marketing, 24(3), 196–208. https://doi.org/10.1108/08876041011040604 ↵
- Følstad, A., & Kvale, K. (2018). Customer journeys: A systematic literature review. Journal of Service Theory and Practice, 28(2), 196–227. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSTP-11-2014-0261 ↵
- Blandino, S. (2016, July). How the Ritz-Carlton delivers exceptional customer service. Stephen Blandino. https://stephenblandino.com/2016/07/how-the-ritz-carlton-delivers-exceptional-customer-service.html ↵
- Sirk, C. (2024, January 25). How the Ritz-Carlton creates a 5-star customer experience. Crm.org. https://crm.org/articles/ritz-carlton-gold-standards ↵
- Alux.com. (2020, March 26). 15 things you didn’t know about the Ritz Carlton [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/3xJRnQVToo4?si=BVlMpS441Q7knJCu ↵
The process of improving service quality and customer satisfaction through cohesive brand interactions.

