Future Horizons: Strategic Planning in Marketing
Strategic Planning in Marketing
To understand strategic planning, it is essential to first define strategy.
What is Strategy?
Although there are many ways to define strategy, in business, we can think of strategy as a guide or road map that outlines how an organization will achieve its long-term goals[1]. It involves making fundamental decisions about the direction of the business and allocating resources to pursue this direction.
With this context, strategic planning in marketing is a comprehensive process that helps organizations define their long-term marketing goals and determine the best approach to achieve them.
“What is Strategy” [8:46 min] by David Kryscynski[2]
If you are using a printed copy, you can scan the QR code with your digital device to go directly to the video: “What is Strategy” [8:46 min] by David Kryscynski

Most Common Reasons Why Startups Fail[3][4][5]
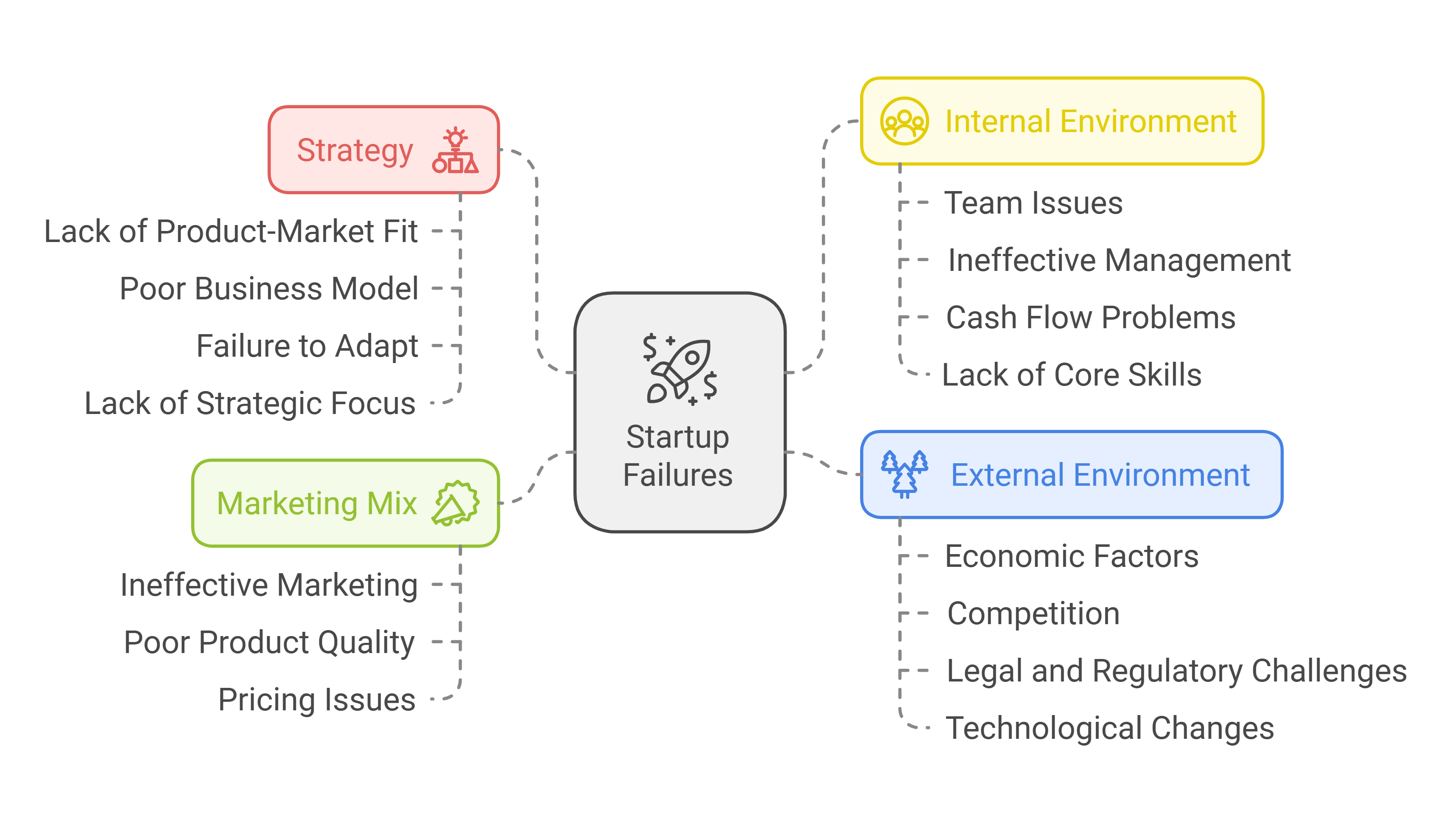
Strategy
- Lack of Product-Market Fit: Many startups fail due to a lack of market need for their product or service. This often stems from insufficient market research and a failure to understand customer needs.
- Poor Business Model: An unsustainable or poorly developed business model is a common cause of startup failure. This includes issues with pricing and cost structures.
- Failure to Adapt: Startups that cannot pivot or adapt to changing market conditions often fail. This includes being unprepared for changes in the market and failing to learn from mistakes.
- Lack of Strategic Focus: Many startups fail due to a lack of clear goals and direction. This can lead to overexpansion or poor resource allocation.
Marketing Mix
- Ineffective Marketing and Distribution: Many startups struggle with inefficient marketing and distribution strategies, including a lack of focus and resources to attract customers. This often includes not having a viable go-to-market strategy.
- Poor Product Quality: Developing a product that does not meet customer needs or expectations can lead to failure.
- Pricing Issues: Incorrect pricing strategies, either too high or too low, can significantly impact a startup’s success.
Internal Environment
- Team Issues: Problems within the founding team — including lack of expertise, experience, and skills — can lead to startup failure. This also includes team disharmony and communication issues.
- Ineffective Management and Leadership: Poor management, including a lack of clear roles and responsibilities among team members, can hinder a startup’s success.
- Cash Flow Problems: Many startups fail due to financial issues, including running out of cash, ignoring cash burn, and inability to raise capital.
- Lack of Core Skills: Startups often fail when they lack essential skills necessary for their business.
External Environment
- Economic Factors: Economic downturns and unfavorable market conditions can significantly impact a startup’s chances of success.
- Competition: Fierce competition and failure to differentiate from competitors can lead to startup failure.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: Startups may face difficulties due to complex legal and regulatory environments.
- Technological Changes: Rapid technological advancements can disrupt a startup’s business model or make their product obsolete.

Effective Strategic Planning
Effective strategic planning can address and prevent many reasons startups fail by providing a comprehensive framework for success.[6][7][8]
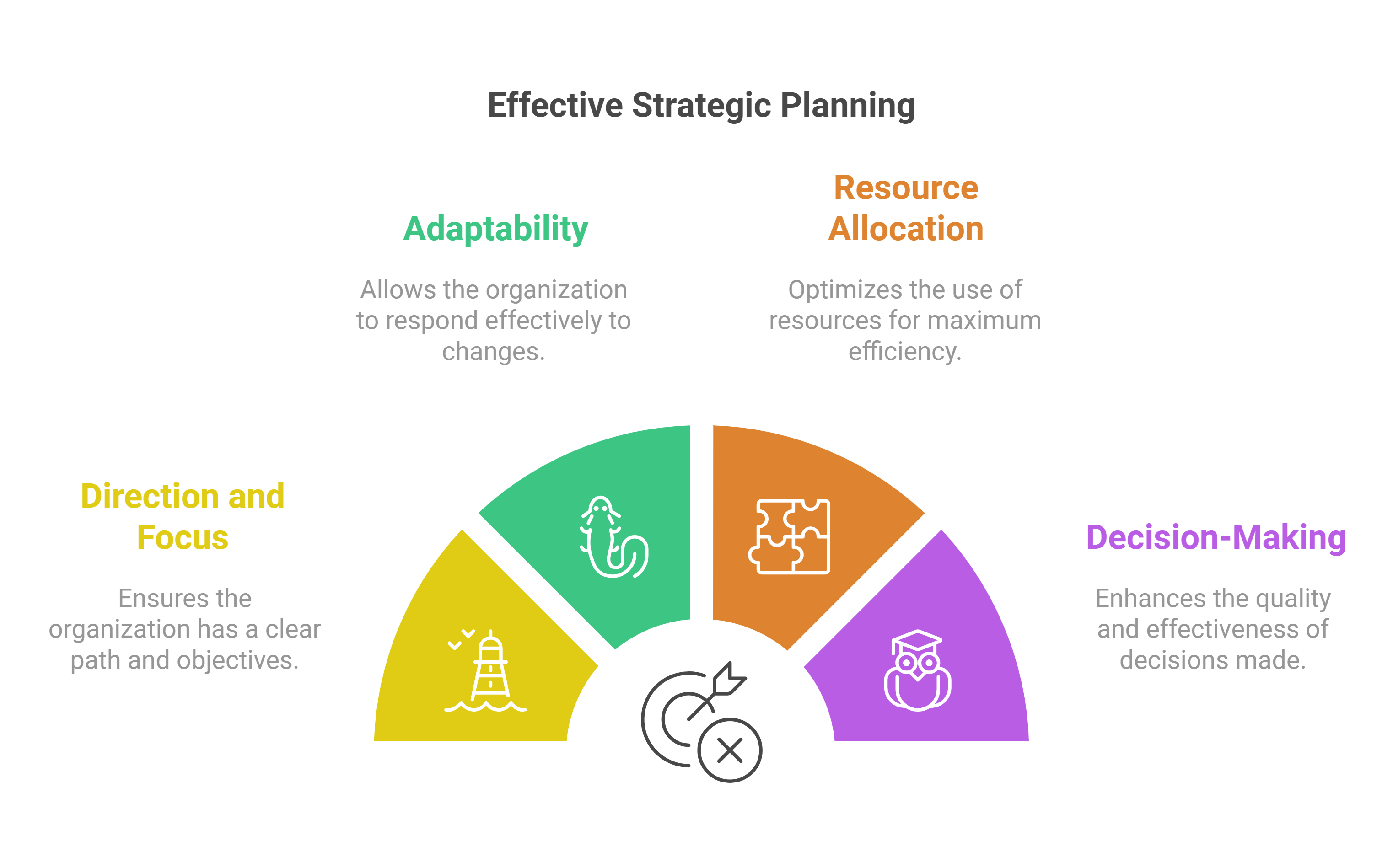
What Does Effective Strategic Planning Do?
Effective strategic planning:
- Provides Direction and Focus: Strategic planning creates a single, forward-focused vision that aligns the entire organization and its stakeholders. This unified direction:
-
- Ensures all employees understand the company’s goals and their role in achieving them
- Prevents conflicting decisions at different organizational levels
- Fosters a greater sense of accountability across the organization
- Helps differentiate essential tasks from distractions, promoting operational efficiency
- Helps Adapt to Changing Conditions: A well-crafted strategic plan enables startups to:
-
- Respond to unanticipated opportunities and threats
- Navigate changing market conditions and technological disruptions
- Continuously assess and improve operations through performance metrics and KPIs
- Gain essential insight into the industry and consumers, forming effective sales and marketing strategies
- Enables Efficient Resource Allocation: Strategic planning helps startups:
-
- Prioritize efforts and allocate limited resources effectively
- Focus on areas that deliver the highest return on investment
- Reduce the risk of cash flow problems and inefficient spending
- Streamline processes, reducing trial and error and preventing wastage of valuable time and resources
- Facilitates Better Decision-Making: By providing a framework for evaluating opportunities and challenges, strategic planning:
-
- Offers a decision-making framework based on predefined objectives and benchmarks
- Helps identify potential risks and devise mitigation plans
- Encourages detailed research on valuable market information
- Enables management to make better and more informed decisions
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Effective strategic planning helps create a sustainable competitive advantage[9][10], which is key to long-term success.
What Is It?
Sustainable competitive advantage (SCA) refers to a company’s ability to consistently outperform its competitors over an extended period by leveraging unique strengths that are difficult for others to copy. Specifically, it is:
- A long-term benefit a company has over its competitors
- Based on unique qualities of the product, service, or company
- Able to withstand competitive pressures over time
- A key factor in a company’s ability to consistently outperform rivals

Where Does It Come From?
We can identify several sources of sustainable competitive advantage, including:
- Resource-based view of the firm
- Organizational capabilities
- Competitive strategies
Resource-Based View of the Firm[11]:
The resource-based view (RBV) of the firm suggests that sustainable competitive advantage comes from a firm’s unique resources and capabilities. These resources can be categorized as tangible (physical assets) or intangible (ideas, knowledge, brands, and processes) and must be:
- Valuable: Should contribute to the company’s ability to create value for customers or reduce costs.
- Rare: Not possessed by many competitors.
- Inimitable: Difficult for competitors to copy or replicate.
- Non-substitutable: No equivalent alternatives available.
Organizational Capabilities
A firm’s organizational capabilities refers to how it can develop sustainable competitive advantage through its superior capabilities in various areas, including:
- Customer loyalty programs
- Strategic location choices
- Efficient distribution and information systems
- Unique or superior products
- Strong vendor relationships
- Exceptional customer service
Competitive Strategies[12][13]:
Competitive strategies are the approaches firms use to leverage their resources and capabilities. Firms can pursue different strategies to achieve sustainable competitive advantage, including:
- Cost Leadership: Offering products or services at a lower cost than competitors.
- Differentiation: This involves offering unique products, services, or experiences that competitors cannot easily match.
Examples: Innovative product features, superior customer service, strong brand reputation, and/or proprietary technology. - Operational Effectiveness: Executing business processes more efficiently.
- Customer Relationships: Building strong, lasting relationships with customers that create loyalty and barriers to competition. This may involve personalized experiences, loyalty programs, and/or exceptional customer support.
- Continuous Innovation: Regularly introducing new products or improving processes.
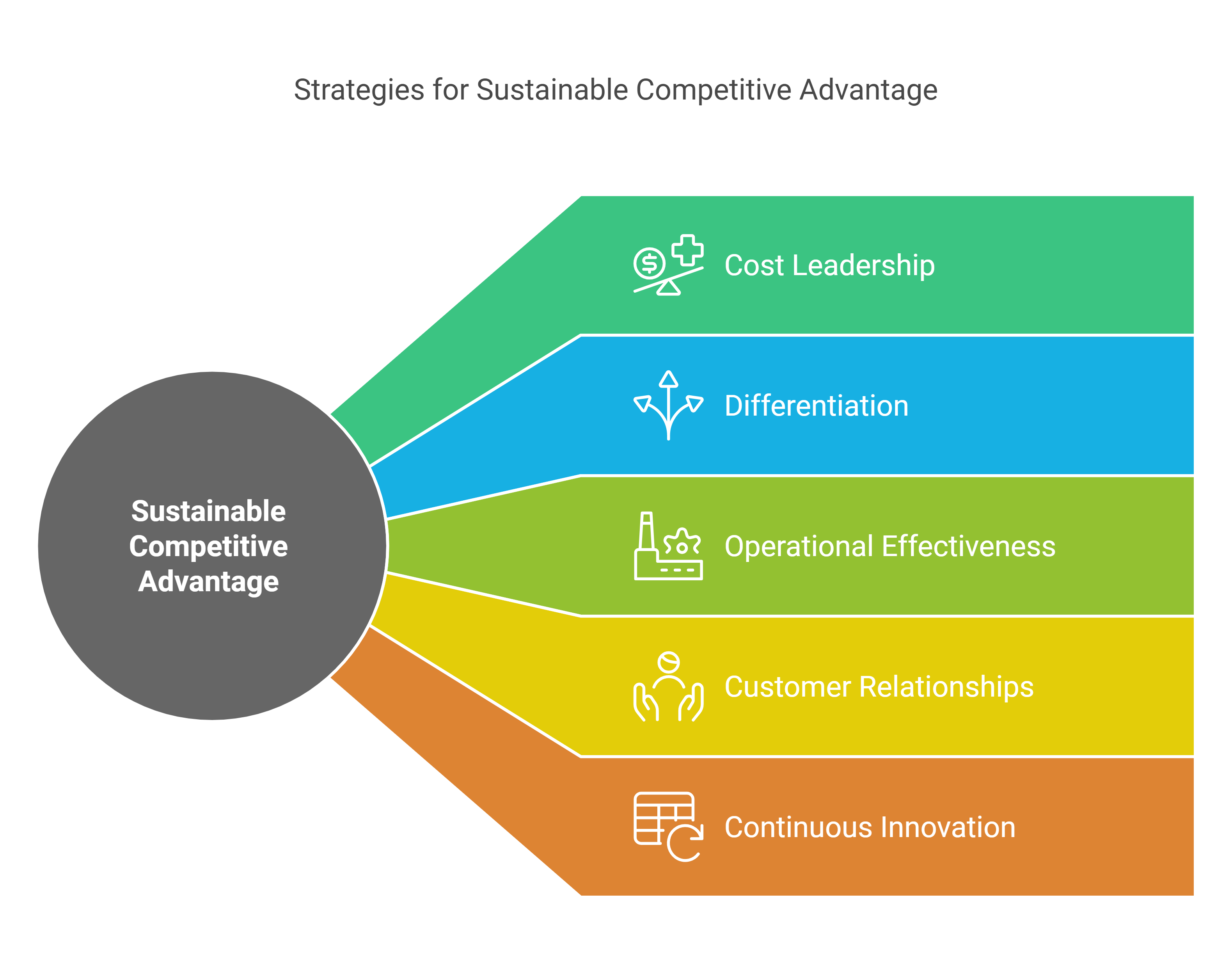
Examples
Competitive Strategies
The following are some commonly used competitive strategies.
Walmart continues to be a prime example of cost leadership. The retail giant leverages its massive scale and efficient supply chain to offer products at lower prices than competitors. According to a 2023 report by Brand Finance, Walmart’s brand value increased to $113.8 billion, making it the world’s most valuable retail brand[14].
Ryanair, the Irish-based low-cost carrier, exemplifies cost leadership in the airline industry. Ryanair’s strategy focuses on offering air travel services at the lowest possible unit cost. They achieve this by eliminating complimentary services (like meals, onboard entertainment, and lounge access), maintaining a single price for all passengers, and reducing costs in procurement by using only a few aircraft models and buying spare parts in bulk. This strategy has helped Ryanair become one of Europe’s largest airlines by passenger numbers[15].
Disney Parks and Resorts demonstrates differentiation through unique experiences and strong brand reputation. Their theme parks offer immersive environments, proprietary technologies like MagicBands, and exclusive character interactions that competitors cannot easily replicate. Disney’s focus on storytelling and attention to detail creates a distinct and memorable experience for visitors[16].
Operational Effectiveness:
Amazon continues to excel in operational effectiveness through its advanced logistics network and automation. In 2023, Amazon expanded its use of AI and robotics in its fulfillment centers, further improving efficiency. The company’s focus on operational excellence has contributed to its continued growth, with net sales increasing by 11% to $134.4 billion in Q2 2023[17].
Customer Relationships:
Netflix demonstrates strong customer relationships through personalized content recommendations and a seamless user experience. In 2023, Netflix introduced new features like password-sharing controls and an ad-supported tier, adapting to changing customer needs. These efforts have helped Netflix maintain its position as a leading streaming service, with 238.39 million paid memberships worldwide as of Q2 2023[18].
Continuous Innovation:
Airbnb demonstrates continuous innovation in the accommodation sector. The company regularly introduces new features and services, such as Airbnb Experiences, which offers unique, locally hosted activities. In response to changing travel trends, Airbnb has also introduced long-term stays and remote work-friendly options. This commitment to innovation has helped Airbnb disrupt the traditional hospitality industry and maintain its competitive edge[19][20].
High-Performing Businesses
High-performing businesses[21] are those that consistently achieve superior results compared to their peers. Sustainable competitive advantage is a key driver of high performance in businesses. It allows companies to consistently outperform their competitors over extended periods, which is a hallmark of high-performance firms.
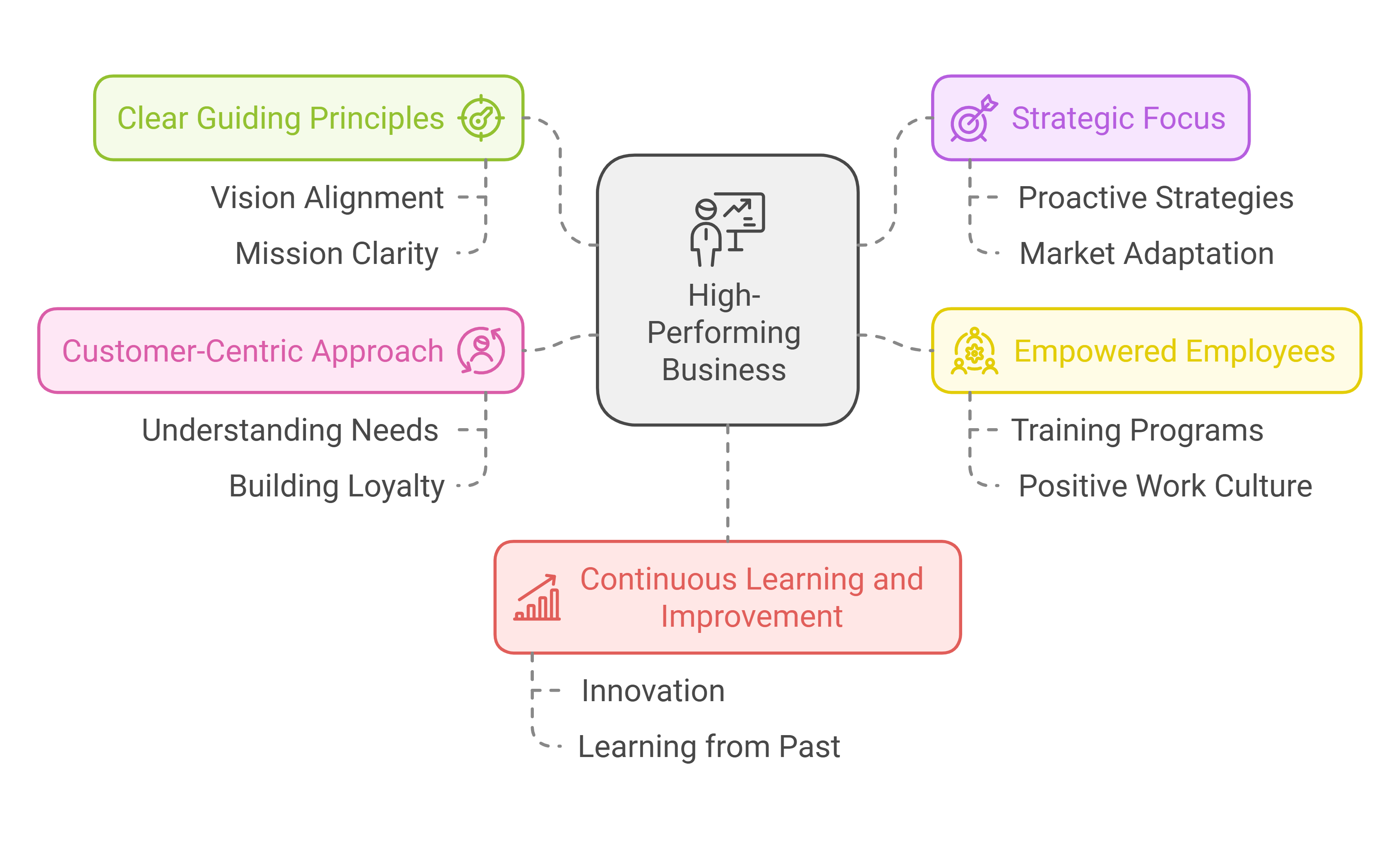
Characteristics of a High-Performing Business
The main characteristics of a high-performing business include:
- Clear Guiding Principles: High-performing businesses have well-defined guiding principles that shape their vision, mission, and goals. These principles provide a clear direction and ensure that every decision aligns with the organization’s core values.
- Strategic Focus: These businesses are strategic in their approach. They are proactive rather than reactive, constantly evaluating their strategies to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Empowered Employees: High-performing companies recognize the importance of their employees and empower them to contribute to the organization’s success. This involves providing training, fostering a positive work culture, and involving employees in decision-making processes.
- Customer-Centric Approach: High-performing businesses prioritize understanding customer needs and delivering exceptional service to build loyalty and long-term relationships
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: High-performing businesses embrace a growth mindset, continuously seeking ways to improve and innovate. They learn from past experiences and view challenges as opportunities for growth.
Mutual Reinforcement
The practices and characteristics that define high-performance organizations are often the same factors that contribute to building and sustaining competitive advantage. Sustainable competitive advantages enable firms to become high performers and high performance provides resources and opportunities to further strengthen and develop new sustainable competitive advantages.

Media Attributions
- Figure 1: “Reasons startups fail” [created using Napkin.ai] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Figure 2: “Failed attempts” [created using DALL-E, Prompt: “create an image reflecting failed attempts at creating a paper boat”] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Figure 3: “Effective strategic planning” [created using Napkin.ai] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Figure 4: “Business Tree Nature” by geralt (2016), via Pixabay, is used under the Pixabay content license.
- Figure 5: “Competitive strategies” [created using Napkin.ai] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Figure 6: “Characteristics of a high-performing business” [created using Napkin.ai] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Figure 7: “Cycle of high performance” [created using Napkin.ai] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Mintzberg, H., Ahlstrand, B., & Lampel, J. B. (2020). Strategy safari: The complete guide through the wilds of strategic management. Pearson UK. ↵
- David Kryscynski. (2015, January 5). What is strategy? [Video]. https://youtu.be/TD7WSLeQtVw?si=OCZpnlrMHbT-oCRu ↵
- Eisenmann, T. R. (2021). Why start-ups fail. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2021/05/why-start-ups-fail ↵
- Szathmári E, Varga Z, Molnár A, Németh G, Szabó ZP, Kiss OE. Why do startups fail? A core competency deficit model. Frontiers Psychology, 15, Article 1299135. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1299135 ↵
- DC, R. (2024, May 14). The 15 most common reasons small businesses and startups fail. Crowdspring. https://www.crowdspring.com/blog/why-businesses-fail/ ↵
- Cote, C. (2020, October 6). Why is strategic planning important? Harvard Business School Online. https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/why-is-strategic-planning-important ↵
- Cecchi-Dimeglio, P. (2023, December 11). 3 ways leaders drive success through strategic planning. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/paolacecchi-dimeglio/2023/12/11/3-ways-leaders-drive-success-through-strategic-planning/ ↵
- Indeed Editorial Team. (2024, June 28). What is strategic planning? (With benefits). Indeed. https://ca.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/what-is-strategic-planning ↵
- Hoffman, N. P. (2000). An examination of the" sustainable competitive advantage" concept: Past, present, and future. Academy of Marketing Science Review, 2000(4). https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=d5711e6a938145b14f5946fee624a977480f3561 ↵
- Huang, K. F., Dyerson, R., Wu, L-Y., & Harindranath, G. (2015). From temporary competitive advantage to sustainable competitive advantage. British Journal of Management, 26(4), 617–636. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.12104 ↵
- Madhani, P. M. (2010). Resource based view (RBV) of competitive advantage: An overview. In P. Madhani (Ed.), Resource based view: Concepts and practices (pp. 3–22). Icfai University Press. https://ssrn.com/abstract=1578704 ↵
- Porter, M.E. (1997). Competitive strategy. Measuring Business Excellence, 1(2), 12-17. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb025476 ↵
- Barney, J. B., & Hesterly, W. S. (2019). Strategic management and competitive advantage: Concepts and cases (6th ed.). Pearson. ↵
- Brand Finance. (2023). Global 500 2023: The annual report on the world's most valuable and strongest brands. https://brandirectory.com/rankings/global/ ↵
- Jhajharia, S. (2023, March 22). 4 cost leadership strategy examples to inspire. Growth Idea. https://growthidea.co.uk/blog/4-cost-leadership-strategy-examples-to-inspire ↵
- Williams, A. (2024, November 12). Disney's generic competitive strategy & growth strategies. Panmore Institute. https://panmore.com/disney-generic-competitive-strategy-intensive-growth-strategies ↵
- Amazon. (2023, August 3). Amazon.com announces second quarter results [Press release]. https://ir.aboutamazon.com/news-release/news-release-details/2023/Amazon.com-Announces-Second-Quarter-Results/ ↵
- Netflix. (2023, July 19). 2023 quarterly earnings: Second quarter earnings — Letter to shareholders. https://ir.netflix.net/financials/quarterly-earnings/ ↵
- PYMTS. (2023, August 4). Airbnb finds ‘jobs via laptop’ enabling long-term rentals. https://www.pymnts.com/connectedeconomy/2023/airbnb-finds-jobs-via-laptop-enabling-long-term-rentals/ ↵
- Aquino, S. (2023, May 23). Airbnb highlights ongoing innovation towards ‘making travel more accessible’ for all. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/stevenaquino/2023/05/23/airbnb-highlights-ongoing-innovation-towards-making-travel-more-accessible-for-all/ ↵
- de Waal, A. (2021). The high performance organization: Proposed definition and measurement of its performance. Measuring Business Excellence, 25(3), 300–314. https://doi.org/10.1108/MBE-04-2020-0064 ↵
The unique, long-term advantage a company holds over its competitors, built on distinctive resources or capabilities that are difficult to replicate.
Approaches organizations use to gain a market advantage, including cost leadership, differentiation, operational effectiveness, and customer relationship management.
A competitive strategy where a company aims to become the lowest-cost producer in its industry while maintaining acceptable quality standards.
A marketing strategy that aims to distinguish a company's products or services from others available in the market to make it more attractive to a particular target market.
Organizations that consistently outperform their competitors by excelling in areas such as strategic focus, operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and employee empowerment.

