Charting the Course: Marketing Foundations
The Marketing Environment
The marketing environment[1] encompasses all the internal and external factors that influence an organization’s decisions and performance. These factors can significantly impact how a company operates, how it markets its products or services, and how it interacts with its customers.
The marketing environment is typically divided into two main categories:
- Internal environment
- External environment
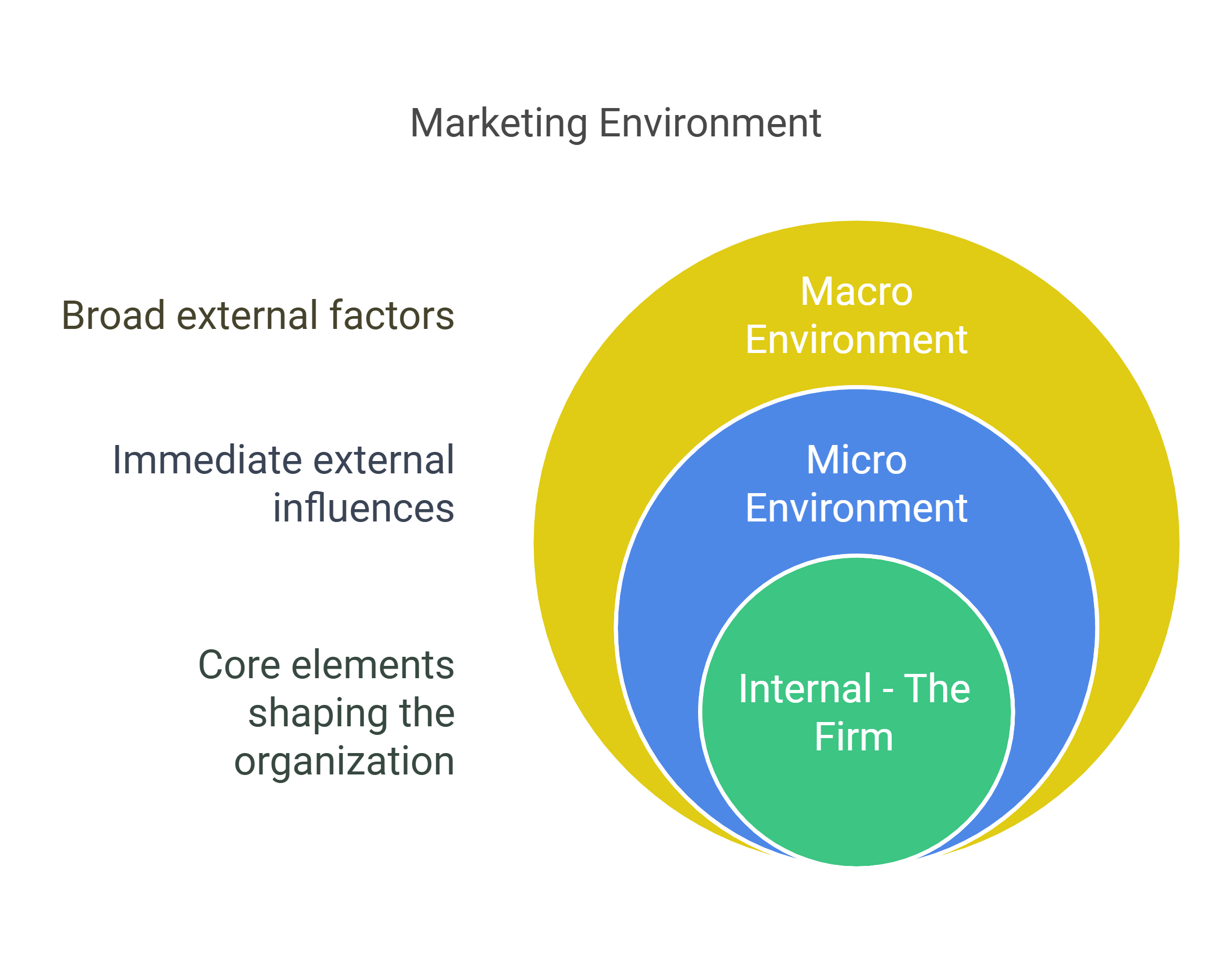
Internal Environment
The internal environment includes factors within the company that can be controlled and managed. These factors are directly related to the organization’s operations and can influence its marketing strategies and decisions.
Key components include:
- Company Culture: The beliefs, values, and behaviours that shape how employees interact and work together.
- Resources: The financial, human, and technological resources available to the company.
- Capabilities: The skills and expertise of the company’s workforce and management.
- Processes: The internal procedures and workflows that determine how tasks are completed.
Example
Internal Environment
A hotel chain with a strong customer-focused culture and well-trained staff can provide exceptional service, enhancing its brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
External Environment
The external environment consists of factors outside the company that it cannot control but must adapt to. These factors are divided into the microenvironment and the macroenvironment.
Microenvironment
The microenvironment consists of factors that are closer to the company and directly affect its ability to serve its customers. These include:
- Customers: The target audience and their preferences, needs, and behaviours.
- Suppliers: Organizations that provide the necessary inputs for the company’s operations.
- Competitors: Other businesses offering similar products or services.
- Intermediaries: Entities that help promote, sell, and distribute the company’s products.
Example
Microenvironment
A travel agency must understand its customers’ preferences for adventure or luxury travel and adapt its offerings to meet these demands.
Macroenvironment
The macroenvironment (often referred to by the acronyms PEST, PESTE, PESTEL, or STEEPLE)[2] consists of broader forces that affect the entire industry and market. These include:
- Political and Legal: Government regulations, policies, and legal issues that impact business operations.
- Economic: Economic conditions — such as inflation, unemployment, and consumer spending — that affect purchasing power.
- Social and Cultural: Societal values, beliefs, and lifestyle changes that influence consumer behaviour.
- Technological: Advances in technology that can create new opportunities or disrupt existing markets.
- Environmental: Ecological and environmental concerns that can affect how businesses operate.
Example
Macroenvironment
A hotel chain may need to adapt to new environmental regulations by implementing sustainable practices to reduce its carbon footprint.
The marketing environment is a dynamic and complex system that influences a company’s ability to market its products and services effectively. By understanding and analyzing both the internal and external factors, organizations can develop strategies to leverage their strengths, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities. This approach enables companies to remain competitive and responsive to changes in the market landscape.
Media Attributions
- Figure 1: “The marketing environment” [created using Napkin.ai] by the author is under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Albrecht, M.G., Green, M., & Hoffman, L. (2023). Factors comprising and affecting the marketing environment. In Principles of Marketing. OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-3-factors-comprising-and-affecting-the-marketing-environment ↵
- Johnson, G., Whittington, R., Scholes, K., Angwin, D., & Regnér, P. (2017). Exploring strategy: Text & cases (11th ed.). Pearson. ↵
Factors within a company that can be controlled and managed, including company culture, resources, capabilities, and processes.
Factors outside a company that it cannot control but must adapt to, divided into microenvironment and macroenvironment.
External factors closely linked to a company, including customers, suppliers, competitors, and intermediaries.
Broader external factors affecting a business, often referred to by acronyms like PEST, PESTE, PESTEL, or STEEPLE.

